Project Management
ARI PD Business Management Systems
What is a project?
A temporary endeavor to produce a unique result. Generally involves limited time, scope, quality, and/or budget, and tradeoffs between those resources.
Contrast with a semi-permanent operational process, which happens over and over in the same way.
Everything is possible but not feasible.Project Management Terms
- Project: temporary endeavor with a unique goal, to create a product, service, or result
- Project Management: planning, organizing. executing, and controlling projects to achieve specific goals and objectives within a defined time frame and budget
- Scope: project boundaries; what is included and excluded from project deliverables
- Stakeholder: anyone with a vested interest in the project
- Schedule: timeline of sequence and duration of project tasks and milestones
- Budget: project's financial plan, including estimated costs and allocated resources
- Risk: uncertain event or condition that can impact the project's objectives
- Quality: degree to which deliverables meet requirements and expectations of stakeholders
- WBS: work breakdown structure
Essential Skills
- Time Management
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Problem-Solving
- Team Management
Essential Qualities
- Leadership
- Strategic Planning
- Problem Solving
- Time Management
- Communication
- Risk Management
- Adaptability
- Budgeting + Cost Control
- Process Improvement
- Technical Expertise
Certifications
- PMP
- PRINCE2
- САРМ
- ACP
- CSM
- ITIL
- PgMP
- MSP
- PMI-RMP
- PMI-SP
Essential Tools
- Gantt Chart
- Network Diagram
- Risk Register
- Issues Log
- RACI Matrix
Approaches
- Waterfall
- Agile
- Scrum
- Lean
- Hybrid
Cash Flow Principles
- Time Value of Money (TVM)
- Net Present Value (NPV)
- Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
- Return on Investment (ROI)
- Payback Period
- Working Capital
- Capital Budgeting
- Financial Leverage
- Breakeven Analysis
- Financial Ratios
Management Process
- Change Request
- Change Evaluation
- Change Approval
- Change Implementation
Project Management
- Analyze needs
- Create list of tasks and dependencies
- Estimate timelines and budgets
- Assign tasks to the sources
- Communicate the plan and make any revisions
- Monitor and report progress (scope/quality), estimate if the project will meet the deadline and budget, and modify the plan as needed
- Deliver results
Process
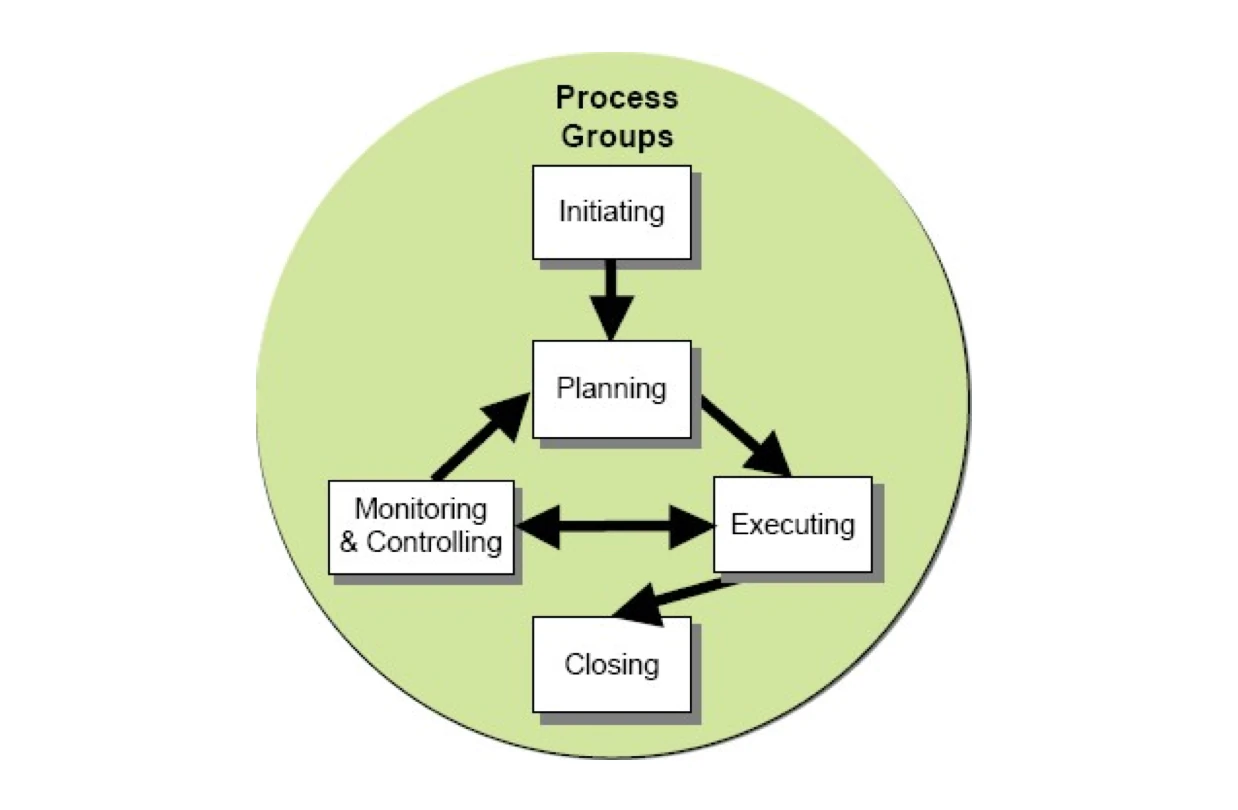
Lifecycle
-
Initiation
- Define purposes + objectives
- Identify stakeholders
- Develop project charter
- Conduct feasibility study
-
Planning
- Define project scope
- Develop WBS
- Estimate time/cost/resources
- Create schedule
- Identify potential risks
-
Execution
- Assign + track tasks
- Manage resource + budget
- Ensure quatty controldget
- Communicate with stakeholders
- Provide progress updates
-
Monitor + Control
- Track progress
- Identify + address deviations
- Manage changes
- Risk assessment + mitigation
-
Closure
- Deliver final product/service/result to customer
- Conduct post-project review
- Document + archive records
- Celebrate successes!
Analyze needs
- Why are we doing this project?
- What business objectives will we achieve?
- What concrete deliverables will we produce?
- What does this project not include (out of scope)?
- What quality level is appropriate for this project?
- Who is involved, both customers of the project (stakeholders) and participants?
- What deadline and budget limits must we meet?
Tasks and dependencies
- Simple projects: checklist
- Complex projects: Work Breakdown Structure
Make sure you know what tasks have to finish before other tasks can start.
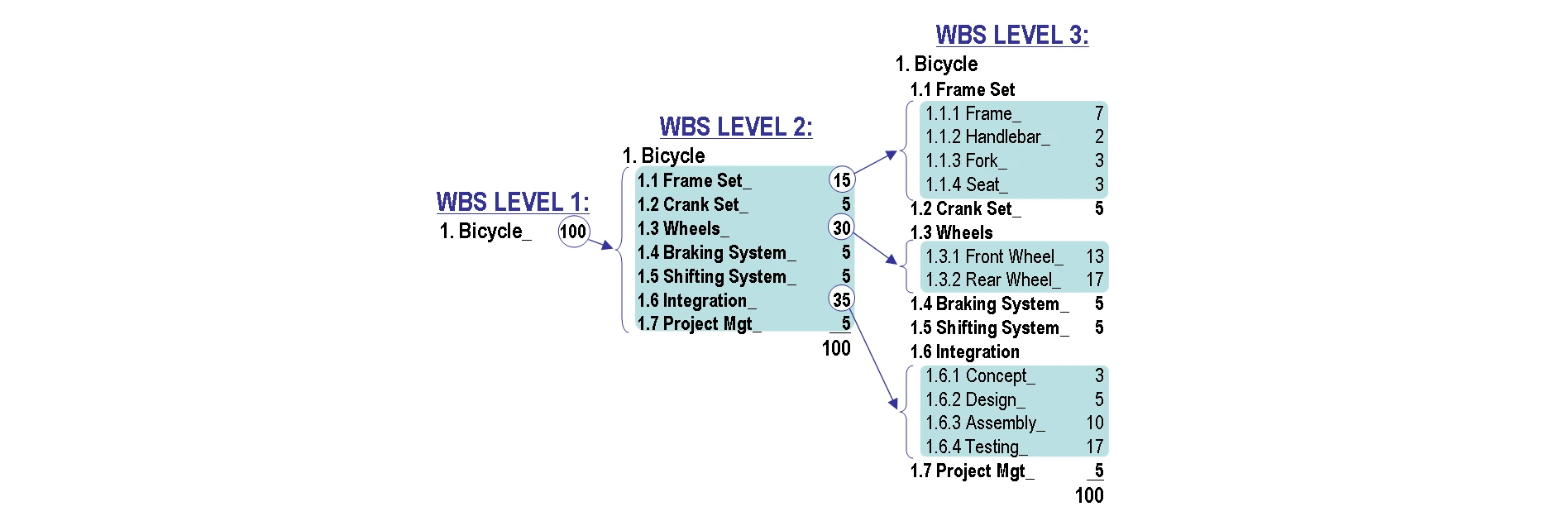
Timelines and budgets
- For each task, estimate how long it will take.
- See what different people can do at the same time.
- Lay out any sequences of tasks with prerequisites.
-
List and/or diagram a full project timeline.
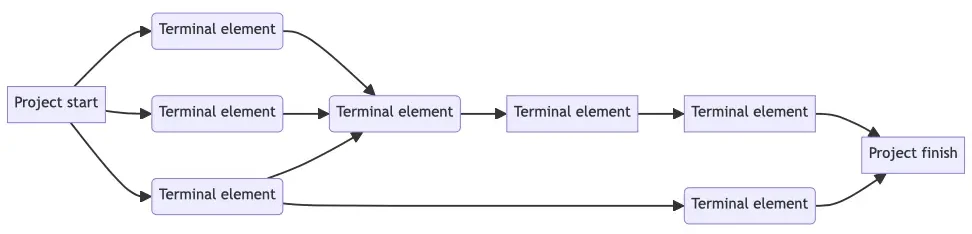
- Estimate budget similarly, if you have a budget.
Assign tasks
- Who would do a good job on this particular task?
- Do they have time to work on it?
- Are their skills better used on other tasks?
- Have they done too much of this kind of task lately? Should they get to learn or practice something different instead? What task assignment makes the team better off overall?
This often changes after asking the team what else they’re working on!
Communicate the plan
This is usually the hardest part.
- What tasks does each participant need to complete? What are the scope, quality, and deadline requirements for each task?
- Do all stakeholders understand the deliverables they’ll receive, the project timeline, and any risks/constraints that could affect the deliverables or timeline? Do they know when to expect progress updates and how to interpret them?
Monitor, report, modify
- Do the project tasks!
- Monitor progress on each task to know if you’re on time / on budget.
- Measure quality along the way, if possible.
- Communicate progress updates regularly to participants and all other stakeholders.
- If you estimate you will miss your deadline, budget, scope, or quality requirements, modify the plan and communicate it again. Overcommunicate early!
KPIs
- Project completion rate
- Budget variance
- Schedule variance
- Scope variance
- Quality metrics
- Resource utilization
- Risk management efficiency
- Stakeholder satisfaction
- Change request volume
- Team member turnover
- Time to market
- Project efficiency
- Return on investment (ROI)
- Customer satisfaction
- Project complexity
- Project flexibility
- Project communication effectiveness
- Milestone achievement rate
- Lessons learned
- Project health index
Deliver results
- Communicate your results to stakeholders via concrete deliverables and discussions.
- Make notes on how to improve the next project, based on your experiences and others’ feedback.
- Thank project participants and tell them how their work was received and what impact it had. Be as specific as possible about their contribution. Celebrate!
Thanks
ARI PD Business Management Systems
Enterprise Software and Solutions on Demand